- Knowledge
Preface:
The trademark opposition system in Namibia is based on the Industrial Property Act No. 1 of 2019 as the core legal framework and is enforced by the Business and Intellectual Property Authority (BIPA). This system aims to balance the interests of trademark owners and the public, prevent malicious registration and conflicts of rights.
1、 Trademark opposition acceptance agency
The Bureau of Commerce and Intellectual Property (BIPA) is the only statutory authority with functions including:
1. Review and Announcement
Conduct formal examination (document compliance) and substantive examination (distinctiveness and conflict search) on trademark applications.
The trademark that has passed the examination is published in the Namibia Industrial Property Journal, and the opposition period starts from the date of publication.
2. Jurisdiction over Objection Cases
Receive objection applications, review legal basis, organize evidence exchange, and make administrative rulings.
3. Proxy mandatory requirement
Foreign objectors must entrust a locally registered trademark agent in Namibia to submit the application (in accordance with Article 15 of the Industrial Property Law).
Local enterprises can submit on their own, but it is recommended to entrust professional agents for complex cases.
Practical tips:
2、 Timing of Trademark Objection
The exercise of objection rights is subject to strict time limits:
1. Announcement period
After the trademark announcement, the objector must submit an opposition application within 60 days (calculated from the day after the announcement), which cannot be restored.
2. Consequences of overdue payment
Trademarks that have not been objected to in a timely manner will be allowed to be registered, and the objector can only protect their rights through the invalidation procedure (applying to BIPA) or litigation in the High Court, which increases the cost by more than three times.
Monitoring suggestion:
Subscribe to bulletin updates through the BIPA official website or use ARIPO (African Regional Intellectual Property Organization) trademark monitoring services to cover Namibian published trademarks.
3、 Basis for Trademark Objection Application
Objections must be based on the statutory reasons stipulated in Articles 34-37 of the Industrial Property Law, with core grounds including:
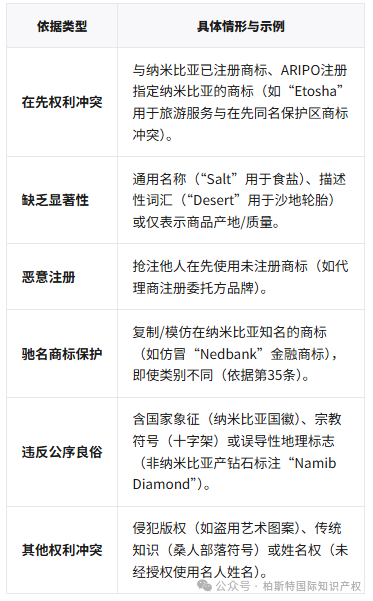
Key points of evidence:
We need to submit a Namibian trademark registration certificate, sales invoice, advertising contract, market research report, etc. to prove the possibility of confusion or malicious intent.
4、 Trademark opposition process
The objection procedure is divided into four stages and is subject to administrative review by BIPA:
1. Submit objection application (1-2 months)
Submit Form IP4 (Notice of Objection), reasons and evidence, and pay official fees (approximately $120).
2. BIPA formal review (1 month)
The integrity of the audit documents shall be reviewed, and the deadline for correction shall be 21 days. Failure to do so shall be deemed as withdrawal.
3. Respondent's defense (3 months)
The objector must submit Form IP5 (defense statement) and counter evidence within 90 days, and may apply for a 30 day extension.
4. Written review and ruling (6-12 months)
BIPA makes decisions based on written materials and may hold hearings if necessary (both parties apply and pay). The ruling results include:
Objection established: The trademark application is rejected, and the objector may appeal to the High Court.
Objection not established: Upon approval of registration, the objector may file a lawsuit with the High Court.
Relief mechanism:
The losing party needs to file a lawsuit with the High Court of Namibia within 30 days after the ruling, and the litigation process takes an average of 2-4 years.
5、 Trademark opposition period
The standard period for objection procedures is 10-18 months, with key variables including:
1. Standard process:
Announcement period (60 days) → Defense period (90 days) → BIPA ruling (6-12 months)
2. Extension factors:
Overseas evidence requires Hague authentication or authentication by Namibian embassies and consulates abroad (an additional 1-4 months);
Hearing procedure (extended for 2-3 months);
BIPA case backlog (average processing delay rate of 25% for objection cases in 2023).
Judicial stage: If entering the High Court for litigation, an additional 2-5 years will be added.
Institutional challenges:
1. Difficulty in protecting traditional knowledge: Government certified community authorization documents (such as Himba tribal patterns) are required.
2. High cost of cross-border evidence: Non English evidence requires dual authentication (notarized by the Namibian embassy or consulate of the source country).
Corporate Practice Strategy
1. Registration Strategy
Designate Namibia through the Madrid System or register using ARIPO (with a separate declaration extending to Namibia at the time of submission).
2. Evidence preparation
Retain local sales vouchers (such as invoices certified by tax authorities) and newspaper advertisements (trademark usage certificates published in The Namibia).
3. Regional collaboration
Monitor ARIPO trademark announcement (opposition period only 3 months) to prevent regional registration risks.
Policy Trends:
Namibia is pushing for the implementation of the Intellectual Property Protocol to the African Continental Free Trade Area Agreement (AfCFTA), and may simplify the objection process in the future. Attention should be paid to BIPA policy updates.




