- Knowledge
Latvia
Trademark opposition system

one
Latvia
Trademark opposition acceptance agency

Latvia implements the EU collaborative jurisdiction system:
1. Administrative supervisory authority
Objection Office of the Latvian Patent Office (LRPV):Responsible for formal review, evidence review, and preliminary ruling
Industrial Property Dispute Committee:Composed of 2 legal experts and 1 technical expert, handling complex case reviews
2. Judicial Authority
Those who are dissatisfied with the administrative ruling can appeal to the Riga Regional Court
The final appeal can be made to the European Union Law Chamber of the Supreme Court of Latvia (a specialized intellectual property panel)
Special requirements for agents:
Applicants within the European Union may entrust an EU registered lawyer to represent them
Non EU applicants must submit their applications through members of the Latvian Patent Agents Association (LRPAA)
Non Latvian documents require authentication and translation by the Ministry of Justice (Chinese documents require dual authentication: Embassy of Latvia, Ministry of Foreign Affairs of China)
objection to a trademark

two
Latvia
Timing of Trademark Objection


1. Official announcement period
After substantive examination, the trademark will be simultaneously announced on the LRPV official website and the eTM Gazette for 3 months
Objection applications must be submitted electronically before 24:00 on the announcement deadline (Eastern European Time EET)
2. Supplementary Objection Period
Within 5 years after trademark registration, supplementary objections can be filed based on malicious registration (with an additional fee of 1500 euros)
3. Grace rule
Can apply for a maximum extension of 30 days (with a daily surcharge of 50 euros)
Force majeure requires notarized proof documents (such as an emergency declaration issued by the embassy)
objection to a trademark

three
Latvia
Basis for Trademark Objection Application


According to Articles 7, 9, and 12 of the Latvian Trademark Law and EU Directive 2015/2436, the statutory grounds for objection include:
(1) Absolutely prohibited reasons
1. Lack of significance
Only composed of the generic name or purely descriptive identifier of the product (such as Balt ā maize white bread)
Unauthorized use of EU registered geographical indications (such as Latvian medicinal wine R ī ga Black Balsam)
2. Violation of public order
Contains national emblems, Soviet era symbols, or content that violates the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights
(2) Relative prohibited reasons
1. Prior conflict of rights
Confusion with registered trademarks in Latvia/EU for identical or similar goods (Nice Classification 12th edition)
Copy unregistered trademarks that are well-known within the European Union (sales data for the Baltic region must be provided)
2. Commercial identification rights
There is substantial similarity with the business name (firm) registered in Latvia
3. Domain name registration
Registering someone else's trademark as a. lv domain (subject to the 2021 Domain Name Dispute Resolution Rules)
(3) Special protection reasons
1. Traditional product labeling
Infringement of protected traditional Latvian product names (such as Sklanrausis beetroot pies)
2. Cultural heritage elements
Unauthorized use of Latvian ethnic costume patterns or folk art symbols
objection to a trademark

four
Latvia
Trademark opposition process


Stage 1: Electronic submission (0-1 week)
Submit an objection statement (in Latvian/English) through the LRPV electronic platform (e-Patent)
Please attach:
Proof of prior rights authenticated by The Hague
Evidence of actual use of the trademark (including invoice with Latvian VAT number)
Baltic Market Analysis Report (when applicable to well-known trademarks)
Stage 2: Formal Review (1-2 weeks)
LRPV will complete the review within 5 working days. Common correction requirements:
Supplement the commodity circulation certificate issued by the Latvian Chamber of Commerce
Update the certification of the European Bar Association for the power of attorney
Stage 3: Substantive defense (1-2 months)
The opposing party shall submit a defense statement within 30 days (with the option to apply for a 15 day extension)
Simultaneously submit a trademark usage plan (certified by a notary office)
Stage 4: Evidence Exchange (2-4 months)
Both parties can submit up to two rounds of evidence (with a 30 day interval between each round)
Accept the EU unified evidence format (such as eEvidence XML standard)
Stage 5: Online hearing (4-6 months)
The Industrial Property Dispute Committee holds a hearing through Zoom (electronic evidence package must be submitted 7 days in advance)
Both parties shall submit a technical comparison report (not exceeding 40 pages, bilingual version)
Stage 6: Administrative adjudication (6-9 months)
Possible ruling outcome:
Completely revoke the opposed trademark (with a success rate of 37% in 2023)
Request for additional differentiation explanation (such as adding regional qualifiers)
Reject the objection application
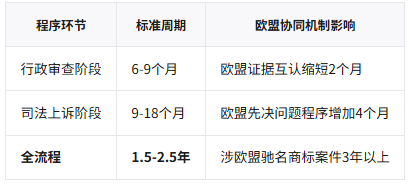
Stage 7: Judicial relief (9-18 months)
The losing party may appeal to the Riga Regional Court (deadline is 30 days)
The average trial time of the Supreme Court is 12-15 months
objection to a trademark

five
Latvia
Trademark opposition period


Time optimization tool:
Fast track: Provide a 6-month acceleration program for small and medium-sized enterprises (annual turnover<1 million euros)
Suspension mechanism: If both parties reach a settlement intention, the procedure can be suspended (with a maximum freeze of 12 months)
Practical operation suggestions
1. Baltic Sea Cooperation Strategy
Real time tracking of trademark announcements in three countries using the EUIPO TMview
Registering a Latvian trademark while applying for an EU trademark (reducing opposition costs)
2. Evidence chain reinforcement
Provide sales records certified by the Latvian Taxation Authority (VID) (including PVN number)
Social media evidence needs to be notarized during the access process and accompanied by a Latvian language abstract
3. Cultural heritage protection
Avoid using ethnic patterns (such as traditional belt patterns of Lielv ā rdes Josta) without authorization
Traditional food trademarks need to obtain traditional product certification from the Ministry of Agriculture in advance
4. Cost control plan
Apply for EU Regional Development Fund (ERDF) subsidies (covering up to 40% of official fees)
Adopting a segmented payment model (40% in the early stage, 40% in the hearing, 20% in the result)
objection to a trademark




