- Knowledge
Kosovo
Trademark opposition system

one
Kosovo
Trademark opposition acceptance agency

Kosovo implements an administrative led jurisdiction system:
1. Administrative supervisory authority
The Objection Division of the Kosovo Intellectual Property Office (KIPO) is responsible for formal examination, evidence review, and preliminary rulings
Industrial Property Appeal Committee: composed of 2 legal experts and 1 technical expert appointed by the Ministry of Justice
2. Judicial Authority
Those who are dissatisfied with the administrative ruling can appeal to the Pristina Commercial Court
Final appeal to the Intellectual Property Division of the Supreme Court of Kosovo (established in 2022)
Special requirements for agents:
Foreign applicants must entrust a registered lawyer from the Kosovo Bar Association to submit objections
Non Albanian/Serbian documents need to be certified and translated by the Ministry of Justice (Chinese documents need to be double certified: Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs Kosovo Office)
objection to a trademark

two
Kosovo
Timing of Trademark Objection


Kosovo adopts EU candidate country transition rules:
1. Official announcement period
After the substantive examination of the trademark, it will be announced on the KIPO official website for 3 months (the original 6-month period will be shortened in 2023)
Objection applications must be submitted in both paper and electronic format before 5:00 PM (CET) on the announcement deadline
2. Supplementary Objection Period
Within 3 years after trademark registration, supplementary objections can be filed based on malicious registration (with an additional fee of 500 euros)
3. Special grace period:
Applicants affected by EU sanctions can apply for a 60 day extension (with proof of bank freeze required)
Force majeure requires certification from the Kosovo Chamber of Commerce
objection to a trademark

three
Kosovo
Basis for Trademark Objection Application


According to Articles 7, 9, and 12 of the Industrial Property Law and the EU harmonization clause, the statutory grounds for objection include:
(1) Absolutely prohibited reasons
1. Lack of significance
Only composed of the generic name or geographical description of the product (such as the name of Dukagjini Plain region)
Unauthorized use of geographical indications of EU candidate countries (such as Rakia fruit brandy)
2. Violation of public order
Contains national symbols, ethnic division symbols, or gender discrimination content (newly added in 2022)
(2) Relative prohibited reasons
1. Prior conflict of rights
Confusion with registered trademarks in Kosovo (using Nice Classification 12th edition)
Copy well-known unregistered trademarks in the Balkans (regional sales proof required)
2. Cultural heritage infringement
Abuse of Kosovo's intangible cultural heritage (such as traditional clothing Opanci patterns)
3. Malicious registration by agents
Unauthorized registration of the principal's trademark by agents in the former Yugoslavia region
(3) Procedural matters
1. Product classification fraud
The application category clearly exceeds the actual business scope (requires submission of a customs HS code comparison table)
2. False priority
Falsely claiming to have priority under the Paris Convention without providing basic application proof
objection to a trademark

four
Kosovo
Trademark opposition process


Stage 1: Mixed submission (0-1 month)
Submit a statement of objection through the KIPO electronic system (in Albanian/Serbian)
Paper originals need to be mailed simultaneously, attached:
Proof of prior rights authenticated by The Hague
Evidence of actual use of the trademark (including Kosovo tax identification documents)
Regional Market Analysis Report
Payment fee: 400 euros (including electronic submission fee)
Stage 2: Formal review (1-2 months)
KIPO will complete the review within 20 working days. Common correction requirements include:
Supplement the commodity circulation certificate issued by the Kosovo Chamber of Commerce
Update Consular Authentication for Proxy Authorization Letter
Stage 3: Substantive defense (3-6 months)
The opposing party shall submit a defense statement within 45 days (with the option to apply for a 15 day extension)
Simultaneously submit a statement of intention to use the trademark (certified by a notary public)
Stage 4: Hearing Procedure (6-12 months)
The Industrial Property Rights Appeals Committee organizes an on-site hearing (evidence package must be submitted 10 days in advance)
Both parties shall submit a final statement (not exceeding 40 pages in bilingual version)
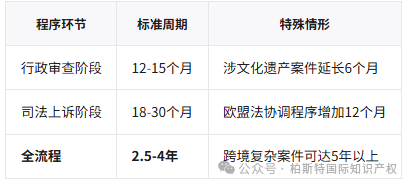
Stage 5: Administrative adjudication (12-15 months)
Possible ruling outcome:
Completely revoke the opposed trademark (with a success rate of approximately 35% in 2023)
Request to modify trademark elements (such as deleting disputed patterns)
Reject the objection application
Stage 6: Judicial relief (15-30 months)
The losing party can appeal to the Pristina Court (deadline is 30 days)
The average trial period of the Supreme Court is 18-24 months
objection to a trademark

five
Kosovo
Trademark opposition period


Timeliness optimization mechanism:
Fast track: Provide 9-month accelerated program for small and medium-sized enterprises (with less than 50 employees)
Mutual recognition of evidence: Trademark data from Albania and North Macedonia can be directly accepted
Practical operation suggestions
1. Regional Compliance Strategy
Apply in advance to the Kosovo Ministry of Culture for a license to use traditional patterns (cost approximately 300 euros)
Avoid using protected geographical names such as Rakia in alcohol trademarks
2. Key points for evidence preparation
Provide cross-border payment records certified by the Central Bank of Kosovo (such as Western Union transaction vouchers)
Social media evidence needs to notarize Albanian language user interaction data
3. Language compliance management
All documents must be prepared in both Albanian and Serbian bilingual versions
Chinese contracts must be accompanied by a certified English abstract
3. Cost control plan
Apply for EU IPA fund subsidy (covering up to 40% of legal fees)
Adopting a segmented payment model (50% start-up fee, 30% hearing fee, 20% outcome fee)




