- Knowledge
A Comprehensive Analysis of the Patent Invalidation System in Spain: Legal Framework, Dual track Procedure, and EU Coordination Strategy
As the fourth largest economy in the European Union, Spain's patent invalidation system integrates the rigor of civil law, EU rules, and local industrial characteristics such as pharmaceuticals and renewable energy. Similar to Italy, Spain adopts a dual track invalidation procedure of administration and judiciary, but its litigation efficiency ranks among the top in Europe. This article systematically analyzes the core logic and practical strategies of the Spanish patent invalidation system from the perspectives of legal basis, procedural path, and evidence rules.
PART .01
Legal basis: Legal grounds for patent invalidity (Ley 24/2015 Spanish Patent Law)
According to Article 102 of the Spanish Patent Law (Ley de Patentes), the statutory circumstances in which a patent may be declared invalid include:
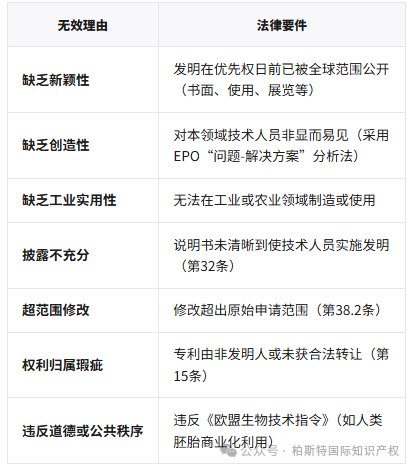
Special provisions:
Pharmaceutical patents:The Supplementary Protection Certificate (SPC) is bound to the basic patent, and if the basic patent is invalid, the SPC will automatically become invalid (Article 114).
Software Patent:Proof of 'technical effects beyond the computer program itself' is required (following EPO case law).
PART .02
Dual track ineffective procedure: administrative objection and judicial litigation
Applicable to:Only applicable to Spanish domestic patents (non European patents).
Key rules:
Objection Window:Submit an invalidation request within 6 months after the announcement of patent authorization (Article 59).
Written review:Both parties submitted evidence and defenses, without an oral hearing.
Time limit for arbitration:A decision is usually made within 12-18 months, with a cost of approximately 3000-10000 euros.
Judgment effectiveness:OEPM may declare all/part of the patent invalid, and the result will be published in the Industrial Property Bulletin.
1. Jurisdiction Court:
First instance: Commercial courts in Madrid and Barcelona (Juzgados de lo Mercantil) (with centralized jurisdiction over national patent cases).
Appeal: Provincial Court of Appeal (Audiencia Provincial).
Final appeal: The Supreme Court of Spain (Tribunal Supremo).
2. Core process:
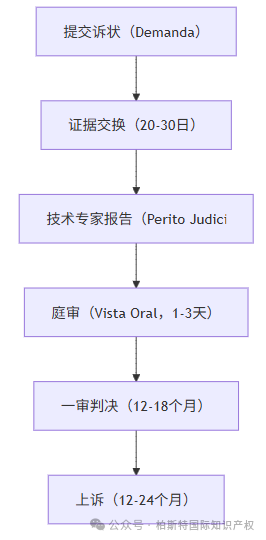
3. Program features:
Compulsory intervention of technical experts: The court designates independent technical experts (with a period of 3-4 months).
Temporary injunction linkage: Patent invalidation lawsuits often go hand in hand with infringement counterclaims (Article 143).
Cost: Ordinary cases can cost 50000 to 150000 euros, while high-tech cases such as medicine can cost up to 300000 euros.
PART .03
Connection with the European Patent System
EPO opposition procedure: Challenge European patents within 9 months, and if successful, Spain will automatically invalidate them.
National procedure: After the objection period expires, invalidation must be filed through the Spanish court (OEPM does not have the authority to handle European patents).
Spain has not yet approved UPCA and does not participate in the UPC system. The invalidity of European patents in Spain is still under the exclusive jurisdiction of its own courts.
Key exception: Spain participates in the effectiveness of a single patent through the Unified Patent Protection Agreement (UP), but the invalidation process still belongs to its own courts.
PART .04
Rules of Evidence and Burden of Proof
Burden of proof:The invalid requester shall bear the responsibility (Article 217 of the Civil Procedure Law).
Evidence type:
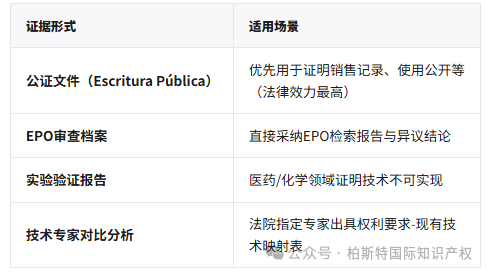
Evidence preservation:You can apply for the Medidas Cautelares (Preventive Evidence Collection) to fix perishable evidence.
PART .05
Ineffective consequences and relief mechanisms
Traceability:After the invalidation judgment takes effect, the patent shall be deemed non-existent from the beginning (Article 107).
Partially invalid:The court may uphold the validity of certain claims (such as invalid independent claims but valid dependent claims).
Reverse compensation for damages:If the patentee has exercised an injunction, they shall compensate the defendant for the losses caused by improper restrictions (Article 140).
Cross border effectiveness:Invalid judgments in Spain can be enforced in member states through the EU Brussels Regulation.
PART .06
Practical Strategies and Industry Applications
Quick and low-cost decision: For patents with weak stability (such as utility models), OEPM administrative procedures are preferred.
Complex technology cases: mandatory judicial procedures for pharmaceutical and communication patents (relying on in-depth analysis by technical experts).
SPC invalid linkage:Synchronize the challenge of basic patents and SPC (Case: Warner Lambert v. Sandoz, Madrid Court of Justice, 2021).
Bolar exception defense:Generic drug companies may invoke Article 61 to implement patents for administrative approval purposes.
EPO file utilization: Obtain EPO opposition reports for same family patents and convert them into evidence in Spanish litigation.
Notarization priority principle: Written evidence such as sales invoices and product manuals must be notarized (otherwise, the proof will be reduced).
- 上一页: In depth analysis of the patent invalidation system in Germany: dual track judicial system, European hub position, and offensive and defensive strategies
- 下一页: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Patent Invalidation System in Spain: Legal Framework, Dual track Procedure, and EU Coordination Strategy




