- Asian

-
trademark law
The current trademark regulations in Malaysia are mainly based on the Trademark Act 2019, which came into effect on December 27, 2019. The Trademark Registry is responsible for managing trademark affairs. Trademark exclusive rights need to be obtained through registration. Trademark registration is not mandatory, but in order to protect the trademark or renew it, it must be registered in accordance with the law.
-
Application principles
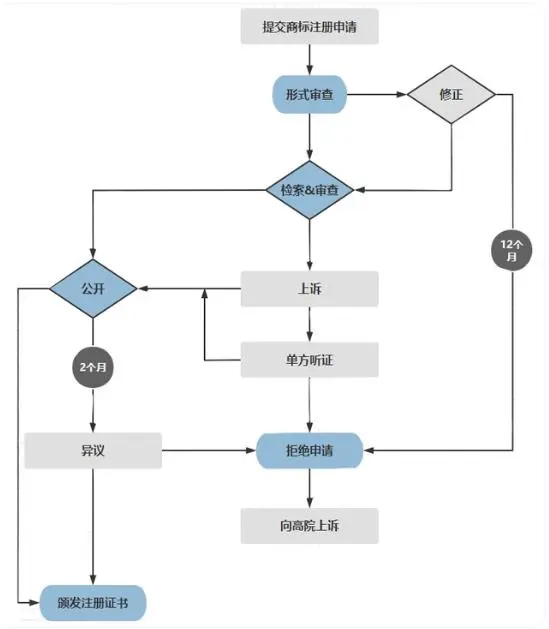
The trademark registration in Malaysia follows the principle of "use first".
-
Duration
The Malaysian trademark is valid for 10 years after registration, starting from the date of application; According to the Trademark Law, renewal can be processed within 6 months before the expiration date, with a grace period of 6 months. Trademarks that have not been renewed after the grace period expires can have their trademark rights revived within 6 months from the expiration date of the grace period; The renewal is valid for 10 years.
-
official language
Malay
-
objection to a trademark
Two months from the announcement date is the objection period, during which any interested party or prior rights holder may raise objections. The main reasons for raising objections are:
1. Conflict with prior trademarks, such as owning a prior registered trademark;
2. The trademark lacks distinctiveness;
3. The trademark has adverse effects;
4. Malicious registration;
5. Conflict with other prior rights, such as trade name rights, design rights, copyrights, personal names, etc.
If there are no objections or objections are not valid during the announcement period, registration can be approved and a registration certificate can be issued. If everything goes smoothly, trademark registration in Malaysia takes about 1 and a half years; If things don't go smoothly and there are objections or rejections along the way, the time will be greatly extended. -
Trademark revocation
If a trademark is revoked, its registration application can be revoked if the prior registrant is aware of the existence of the registered trademark. However, in some special circumstances, the trademark registration applicant may withdraw the trademark registration application. The main reasons for trademark revocation include:
1. Violation of trademark law;
2. The trademark has obvious unreasonable use;
3. The trademark is registered without permission;
4. Revoked due to improper registration. -
Trademark classification
Currently, Malaysia adopts the Nice Classification 11th edition of product and service descriptions and accepts applications for multiple categories in one form. The elements that can be registered as trademarks in Malaysia include: text, name, graphics, color, letters, numbers, color combinations, three-dimensional shapes, sound, etc.
-
Registration restrictions
1. The name of an individual or company presented in a special way;
2. Signature of the applicant or their senior colleagues in the business;
3. The general meaning does not involve words that represent the characteristics or quality of goods or services, geographical names, or surnames;
4. Other significant indicators.
5. Registered trademarks shall not cause confusion or misidentification among the relevant public, shall not harm national interests or security, and shall not contain defamatory or offensive content;
6. It is not allowed to register similar words such as "patent", "registration", "industrial design", "copyright" as trademarks. -
other
1. Trademarks in Malaysian applications cannot be transferred.
After the effective date of the 2019 Trademark Law, new applications submitted from December 27, 2019 will be subject to a one-time payment of official fees. For trademark registration applications submitted before the new law came into effect but not yet registered, the official fees will still be paid in stages according to the old law.
Malaysia is a signatory to international intellectual property treaties such as the Paris Convention and the Nice Agreement. It joined the Madrid Protocol on December 27, 2019, so trademark registration can be processed through "single country registration" or "Madrid international registration".
1. Trademark design;
2. Application category and specific trademark address;
3. Applicant's name and address (in English);
4. Power of attorney;
5. Proof of Priority Document (If priority is declared, this document and its Malay translation are required, which must be signed and confirmed by a professional translator with translation qualifications in Malaysia).




